
 Urinary
Antiseptics.
Urinary
Antiseptics.
Compiled and Edited by Ivor Hughes
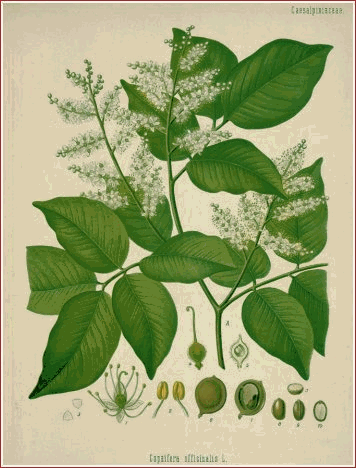
Images. Copaiba and Uva-ursi
COPAIBA and other VEGETABLE URINARY ANTISEPTICS.
Dose
: 0.6 to 2 ml. (10 to 30 minims). Foreign Pharmacopoeias: In Belg., Cz., Egyp., Ger., Nor., Span., and Swiss. The oleoresin obtained from the trunk of Copaifera lansdorfii and other species of Copaifera (Leguminosae). The most important varieties are known as Para, Maranham, Maracaibo, and Savanilla copaiba. A yellow to golden-brown viscous liquid with a characteristic odour and a slightly bitter, acrid, persistent taste. Wt per ml. 0.958 to 0.993 g.Miscible with dehydrated alcohol, ether, carbon disulphide, and fixed and volatile oils; soluble in an equal volume of light petroleum (b.p. 50� to 60�) but precipitated on adding more solvent. That known as Para copaiba is transparent, yellowish, and contains 60 to 90% of oil. It is thinner than the Maracaibo variety, which is brownish and somewhat fluorescent and contains about 45 % of oil.
Uses. Copaiba is carminative and after absorption it is excreted by the bronchioles and kidneys. It has been used as a urinary antiseptic in chronic cystitis and gonorrhoeal urethritis, but it has an irritant action on the mucous membrane of the gastro-intestinal tract and may give rise to digestive disturbances and to a morbilliform rash. In excessive doses it may cause vomiting, purgation, strangury, and haematuria. Albuminuria may be simulated by precipitation of the resin acids with nitric acid; it may be distinguished by the addition of alcohol which dissolves the resins. Because of its unpleasant taste copaiba is best given in gelatin capsules.
Copaiba Oil (B.P.C. 1934). Ol. Copaib.
Dose:
0.3 to 1.2 ml. (5 to 20 minims). An oil distilled from copaiba. It is a
colourless or pale yellow, volatile liquid with a pepper-like odour and
bitter, pungent taste. Wt per ml. about 0-90 g. Soluble 1 in 1 of dehydrated
alcohol and 1 in 20 of alcohol (90%).
Uses. It
has been used for the same purposes as copaiba and may be administered in
gelatin capsules or as an emulsion.
Cubeb (B.P.C.). Cubeba; Cubeb Berries; Cubeb Fruit; Tailed Pepper.
Dose: 2
to 4 g. (30 to 60 grains).
Foreign Pharmacopoeias: In Span, and Swiss. Also in Ind. P.C. and
U.S.N.F.
The dried, unripe fully grown fruit of Piper Cubeba (Piperaceae),
containing not less than 15% v/w of volatile oil. Powdered Cubeb (B.P.C.)
contains not less than 12% v/w of volatile oil. Protect from moisture in
a cool place.
Uses. It
has an action similar to that of copaiba and was formerly employed as a
urinary antiseptic. As an expectorant it has been used in sub acute and
chronic bronchitis, usually in the form of lozenges.
Oleores. Cubeb. (B.P.C. 1949, Ind. P.C.). Oleoresin of Cubeb.
The ether-soluble extractive of cubeb. Protect from moisture in a cool
place.
Dose: 0.3
to 2 ml. (5 to 30 minims).
Cubeb Oil (B.P.C. 1949, Ind. P.O.). Ol. Cubeb.
Dose:
0.3 to 1.2 ml. (5 to 20 minims).
An oil obtained by distillation from cubeb. It is a colourless, pale yellow,
or bluish-green liquid with a warm characteristic odour and a camphoraceous
taste. Wt per ml. 0.905 to 0.925 g. Soluble 1 in 18 of alcohol (90%);
miscible with dehydrated alcohol. Protect from light in a cool place.
Uses. It was
formerly employed, usually as an emulsion or in capsules, as a urinary
antiseptic.
Sandalwood Oil (B.P.C. 1949). Ol. Santal.; Oil of Santal Wood.
Dose:
0.3 to 1 ml. (5 to 15 minims).
Foreign Pharmacopeias: In Belg., Dan., Egyp., Ger., Nor., Span., Swed.,
and Swiss. Also in Ind. P.C.
An oil obtained by distillation from the heartwood of Santalum album
(Santalaceae). It is a pale yellow or nearly colourless, viscid liquid with
a peculiar, faint, persistent odour and unpleasant, nauseous taste,
containing not less than 2% w/w of esters and not less than 90% w/w of free
alcohols. Wt per ml. 0.968 - 0.983 g. Soluble 1 in less than 1 of alcohol
(90%), 1 in 5 of alcohol (70%), in chloroform and ether. Protect from light
in a cool place.
Uses. It
was formerly employed, often in conjunction with cubeb, as a urinary
antiseptic.
Caps. Ol. Santal. (B.P.C. 1949). Capsules of Sandalwood Oil.
Unless otherwise specified, 10-minim capsules are supplied.
Australian Sandalwood Oil (B.P.C. 1949). Ol. Santal. Austral.
Dose:
0.3 to 1 ml. (5 to 15 minims).
An oil obtained by distillation from Eucarya spicata ( = Santalum spicatum)
(Santalacea?). It is a colourless or pale yellow oily liquid with a
characteristic odour and unpleasant taste, containing not less than 90% w/w
of free alcohols. Wt per ml. 0.964 to 0.974 g. Soluble 1 in 3 to 6 of
alcohol (70%). Protect from light in a cool place.
Uses. It has been used for the same
purposes as Sandalwood oil. Oils of sandalwood are also used in perfumery.
 Bearberry
(B.P.C. 1934). Uva Ursi; Bearberry Leaves; Busserole;
Barentraubenblatter.
Bearberry
(B.P.C. 1934). Uva Ursi; Bearberry Leaves; Busserole;
Barentraubenblatter.
Foreign Pharmacopoeias: In Belg., Cz., Dan., Egyp., Fr., Ger., Hung.,
Jap., Jug., Nor., Pol., and Swiss.
The dried leaves of the bearberry, Arctostaphylos uva-ursi (Ericaceae).
Uses. It is
diuretic and astringent and exerts an antiseptic effect on the urinary
tract. It has been employed in urethritis and cystitis as a fresh infusion
(1 in 20; dose: 15 to 30 ml.), a concentrated
infusion (1 in 2�; dose:
2 to 4 ml.), and a liquid extract (1 in 1; usual
dose: 2 ml.).
Boldo (B.P.C. 1934). Boldo Leaves.
Dose:
60 to 200 mg. (1 to 3 grains).
Foreign Pharmacopeias: In Belg., Chil., Egyp., Fr., and Span.
The dried leaves of Peumus boldus (Monimiaceae). It contains the
alkaloid boldine (about 0-1%), the glycoside boldin or boldoglucin, and
about 2% of volatile oil.
Uses. It
has been employed as a diuretic in the form of a tincture (1 in 10; dose:
0.5 to 2 ml.) or liquid extract (1 in 1; usual dose: 1 ml.). The alkaloid
boldine has been used in the treatment of hepatic congestion.
![]()